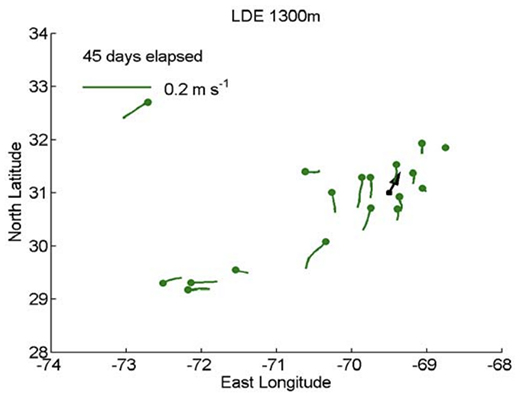
SOFAR float trajectories (green worms) and horizontal velocity measured by a current meter
(black vector) during the Local Dynamics Experiment conducted in the Sargasso Sea.
This essay introduces the two methods that are widely used to observe and analyze fluid flows, either by observing the trajectories of specific fluid parcels, which yields what is commonly termed a Lagrangian representation, or by observing the fluid velocity at fixed positions, which yields an Eulerian representation. Lagrangian methods are often the most efficient way to sample a fluid flow and the physical conservation laws are inherently Lagrangian since they apply to moving fluid volumes rather than to the fluid that happens to be present at some fixed point in space. Nevertheless, the Lagrangian equations of motion applied to a three-dimensional continuum are quite difficult in most applications, and thus almost all of the theory (forward calculation) in fluid mechanics is developed within the Eulerian system. Lagrangian and Eulerian concepts and methods are thus used side-by-side in many investigations, and the premise of this essay is that an understanding of both systems and the relationships between them can help form the framework for a study of fluid mechanics.
